


Answers to All of Your Alpha-Gal Syndrome Questions
An alpha-gal diagnosis can turn your life upside down overnight. If you’re not already eating a vegan diet, having to immediately cut all mammalian meat products – like beef, pork, and lamb – from your diet can be jarring. And if you react to cow’s milk and have to further eliminate cheese, yogurt, ice cream, and chocolate from your diet, it can be downright depressing. Here are answers to the most commonly asked questions about living with alpha-gal syndrome.

What is Alpha-Gal Syndrome?
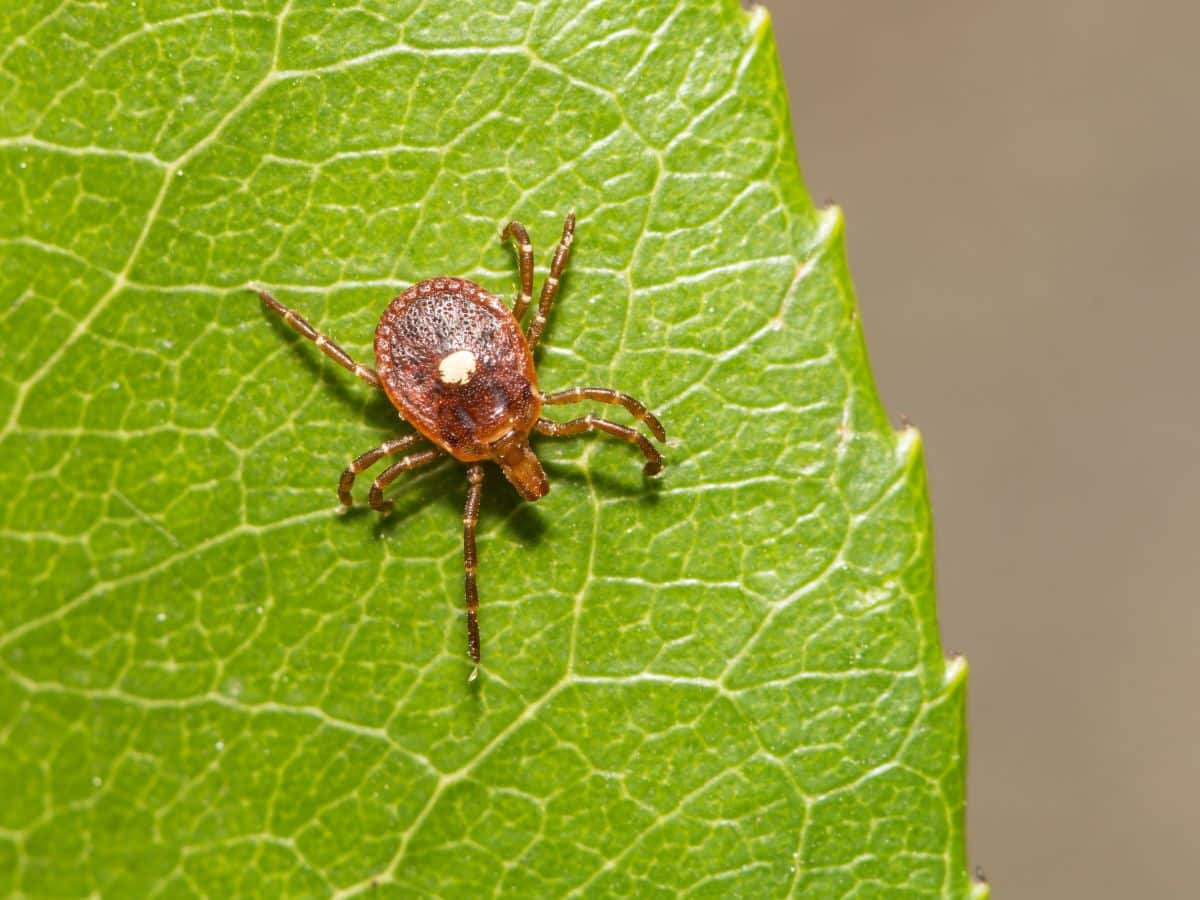
Alpha-gal syndrome is a tick-borne disease that results in a food allergy to meat, dairy, and other products made from mammals like cows, pigs, and sheep. It is also known as alpha-gal allergy, mammalian meat allergy, red meat allergy, or tick bite meat allergy.
In the United States, alpha-gal syndrome is most commonly caused by a bite from the lone star tick. Easily identified by a white dot on its back, this little bloodsucker is carried by deer in the eastern and south-central regions of the US. In Europe, Australia, and Asia, the alpha-gal molecule has been found in different species of ticks, including the castor bean tick, kangaroo tick, and Asian longhorned tick.
When one of these nasty little buggers bites you, it injects a sugar molecule called alpha-gal into your body. In some people, this unfortunate incident results in an allergic reaction after consuming beef, pork, lamb, dairy, gelatin, collagen, or other mammalian products. An allergic reaction to alpha-gal can vary from annoyingly uncomfortable to life threatening.
Want Alpha-Gal Safe Recipes and More?
Sign up for the weekly newsletter!
Thank You for Subscribing!
When Was Alpha-Gal Syndrome Discovered?
The TL;DR answer is that Dr. Thomas-Platts-Mills discovered a red meat allergy transmitted by ticks in 2007. You can read more here about how a cancer drug approved a few years prior helped him connect the dots and how his research lab collaborated with others around the world to realize that the syndrome wasn’t isolated to the Southeastern US.
What Causes Alpha-Gal Syndrome?
In the United States, this food allergy typically develops after a person is bit by the lone star tick. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), other ticks may also contribute to alpha-gal syndrome.
In Europe, Australia, and Asia, the alpha-gal molecule has been found in different species of ticks, including the castor bean tick, kangaroo tick, and Asian longhorned tick.
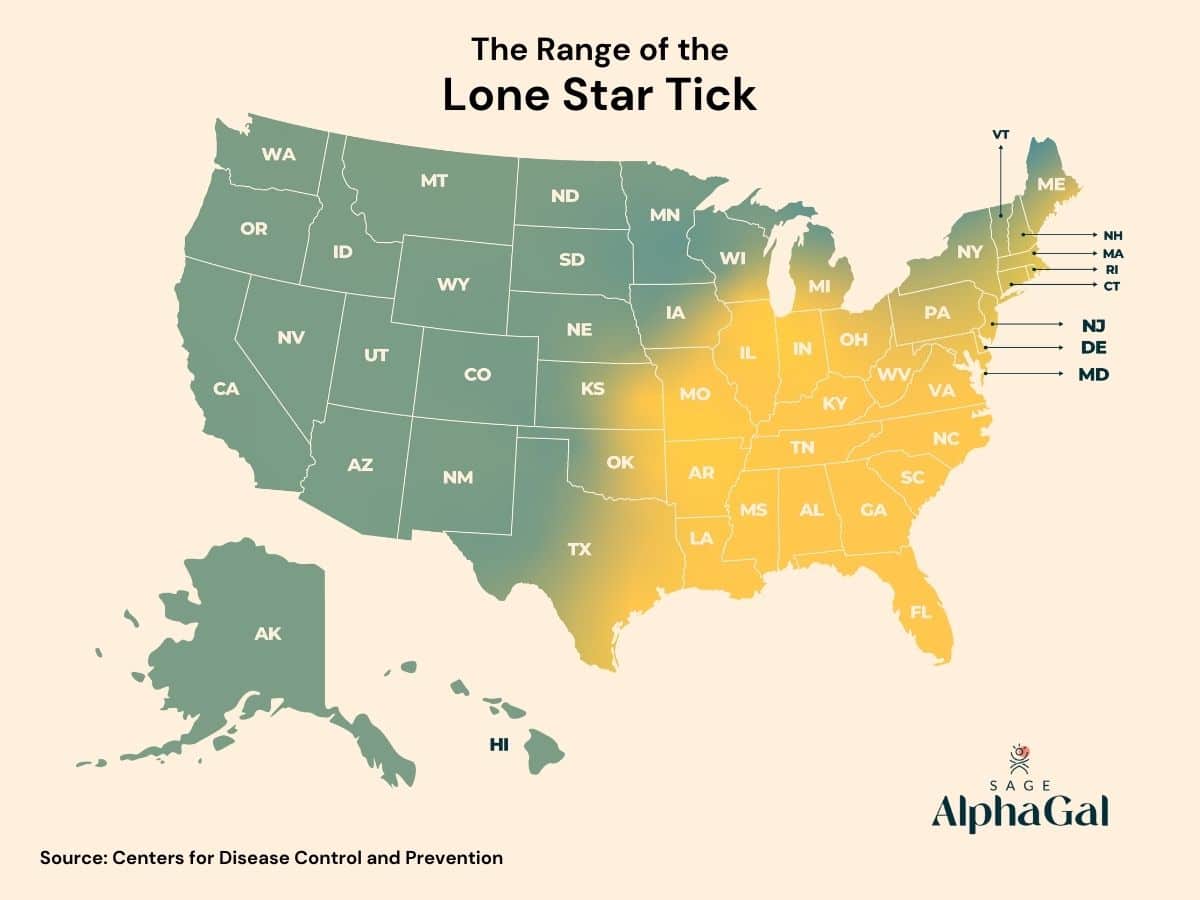
Where Are Lone Star Ticks Found?
According to the CDC, the nasty little lone star tick makes its home primarily in the Eastern, Southeastern, and Midwestern US. However, it’s been expanding its historical range north and west so that lone star ticks can now be found as far north as Maine and Michigan and as far west as Central Nebraska, Kansas, and Texas. At this time, the lone star tick’s range remains east of the Rocky Mountains.
How Long After a Tick Bite Does Alpha-Gal Develop?
Most food allergies cause quick reactions. For example, a person allergic to peanuts or shellfish typically experiences a reaction within minutes of consuming peanut butter or lobster. But it’s not uncommon for an alpha-gal reaction to take several hours to appear.
And reactions can vary widely by person. You may have alpha-gal syndrome if you experience any of the following symptoms within three to six hours after enjoying a big plate of biscuits and sausage gravy, a platter of Kansas City barbeque, or an ice cream sundae for two:
- An itchy rash or hives
- A runny nose, sneezing, or headache
- Swelling in your lips, tongue, or throat
- Wheezing or shortness of breath
- Gastrointestinal symptoms including stomach pain, diarrhea, nausea, and/or vomiting
Can Alpha-Gal Get Worse?
According to researchers and medical professionals, alpha-gal symptoms can become more severe over time. Based on my personal experience and conversations with other alpha gals in my life, it’s true – and continuing to consume mammalian products only worsens the condition. Once you’ve been diagnosed with alpha-gal syndrome, the best way to manage your symptoms is to avoid all allergy-triggering foods and to avoid additional tick bites.
Sage Advice: Use the form below to print a free trigger tracker that you can use to document everything you eat and drink for a month. Record any reactions and list any potential triggering ingredients. Share your food diary with your physician and/or dietician to identify patterns and adjust your diet accordingly.

Food Allergy Trigger Tracker
Identify your alpha-gal triggers and understand your sensitivity to them with this free daily food diary and symptom tracker
Thank you!
Please check your email for your free food allergy trigger tracker.
How Common is Alpha-Gal Syndrome?
Most people with alpha-gal syndrome in the United States live in the south, east, and central regions of the country where the lone star tick is most commonly found. Approximately three percent of Americans (around 10 million people) currently suffer from alpha-gal syndrome.
How Do You Test for Alpha-Gal Syndrome?
If you suspect that you have alpha gal syndrome, talk to your physician. You know your body better than anyone else, and many physicians are still unaware of alpha-gal. Be sure that your doctor orders the right test – and not the one for Fabry disease, a similar condition – by sharing these lab codes:
- Quest Diagnostics | Alpha-Gal Panel Test Code: 10555
- Labcorp | Alpha-Gal IgE Panel Test Code: 650003
After inquiring about your exposure to ticks and your symptoms, your doctor will most likely order a blood test to measure the amount of alpha-gal antibodies in your bloodstream.
If your alpha-gal syndrome blood test shows an antibody level of more than 0.10 kU/L for alpha-gal (officially known as galactose-alpha-1,3-galactose), your test is likely considered to be positive.
How Much Does an Alpha-Gal Test Cost?
The cost of your alpha-gal syndrome blood test is likely dependent on your health insurance coverage. Because the test must be requested via a physician, be sure to ask about your anticipated out-of-pocket costs before getting your blood drawn.
How to Manage Alpha-Gal Syndrome
The best way to manage alpha-gal syndrome is to not consume mammalian meat like beef, pork, lamb, and bison. Don’t overlook sneaky sources of mammalian meats such as gelatin and collagen. It’s also best to avoid foods with carrageenan. Although it’s a plant-based ingredient derived from an edible red seaweed, it contains the alpha-gal epitope and may trigger your alpha-gal allergy.
While many alpha gals can tolerate dairy products, if you cannot, you will also need to avoid foods like milk, cheese, cream, and yogurt made from cow’s milk, sheep’s milk, and goat’s milk to manage your alpha-gal allergy.
Does Alpha-Gal Syndrome Make You Tired?
Alpha-gal syndrome is a food allergy that can present itself in a variety of ways. An allergic response to alpha-gal may include itching, hives, nausea, diarrhea, abdominal pain, chronic fatigue, and swelling. People who have a severe reaction to alpha-gal can experience anaphylactic shock.

What Foods to Avoid If You Have Alpha-Gal Syndrome
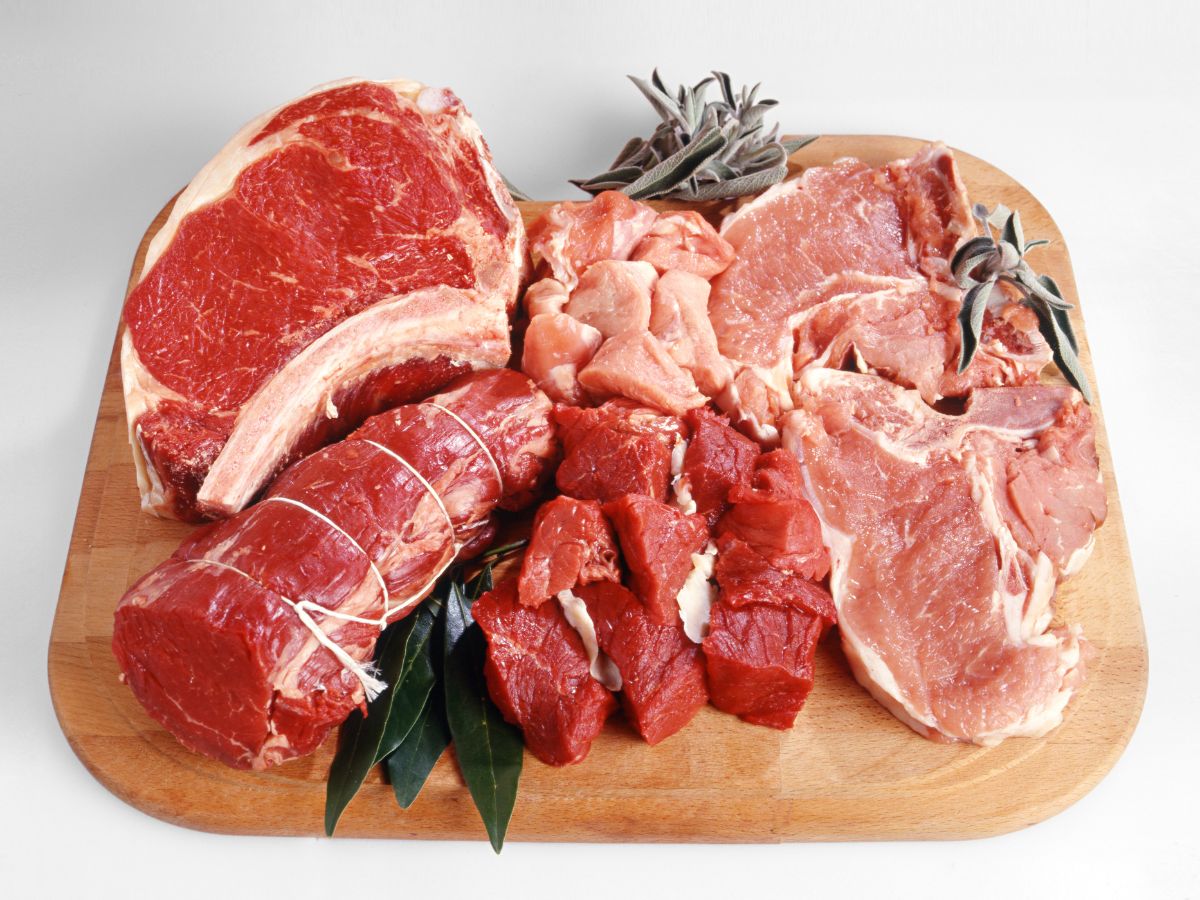
As a general rule, people with an alpha-gal allergy should avoid all mammalian meats, dairy products (if sensitive to them), and by-products, which include beef, pork, lamb, mutton, bison, venison, goat, and rabbit meat. They should also avoid foods with ingredients derived from mammals, like gelatin and collagen. Additionally, people with alpha-gal syndrome should avoid medicine capsules containing gelatin and beauty products with collagen.
Alpha gals who cannot tolerate dairy products also need to avoid all milk, cheese, yogurt, and other products made from cow’s, sheep’s, or goat’s milk.
What Foods Can You Eat If You Have Alpha-Gal?
Alpha gals need to avoid all mammalian meats – like beef, pork, bison, and lamb – as well as products that include related ingredients like gelatin and beef broth. It’s also important to avoid carrageenan, an extract from red seaweed used to thicken drinks and plump up pudding. Why do alpha gals need to avoid carrageenan? Because this unique plant-based ingredient contains the alpha-gal epitope that can cause a reaction for some people with alpha-gal.
So what foods can you eat if you have alpha-gal? If you are an alpha gal who cannot tolerate dairy, then you can summarize your alpha-gal diet as vegan + eggs + poultry + fish. If you’re an alpha gal who can tolerate dairy, then you can summarize your diet as vegetarian + poultry + fish.
Related Article: Alpha Gal Food List: Allergy-Friendly Options for Alpha-Gals
Does Alpha-Gal Go Away?
One of the first questions many people living with alpha-gal syndrome ask is, “How long does alpha-gal last?” As a general rule, once you have alpha-gal syndrome, you will live with it for the rest of your life. However, by avoiding the foods and products that trigger an allergic reaction and by avoiding additional tick bites, some alpha-gal sufferers have seen their symptoms decrease over time.
On the other hand, alpha gals bitten by additional lone star ticks can experience greater allergic reactions over time. After additional tick bites, the ground beef taco that once caused you to break out in hives or writhe in pain may require you to carry an EpiPen in case you go into anaphylactic shock.

Is Alpha-Gal Syndrome Contagious?
Because the alpha-gal sugar molecule is not found in people (or fish, reptiles, or birds), you cannot contract it from a person who is alpha-gal positive. The best protection against alpha-gal syndrome is to avoid tick bites, especially in lone star tick country.
Is Alpha-Gal Syndrome Genetic?
No, alpha-gal is a tick-borne illness that results in an allergy to mammalian meats like beef, pork, lamb, bison, elk, goat, and rabbit.
Is There a Cure for Alpha-Gal Syndrome?
People living with alpha-gal syndrome often ask, “Can alpha-gal be cured?” Unfortunately, there is currently no cure for alpha-gal syndrome. However, you can manage your symptoms by avoiding mammalian meat (and mammalian milk if you have a sensitivity to it). It’s also important to avoid new tick bites, as they can reactivate and even increase allergic reactions to alpha-gal.
Some patients are exploring Soliman Auricular Allergy Treatment (SAAT), a fairly new acupuncture treatment for allergies. However, the effectiveness of this treatment is debatable. While acupuncturists report it to be an effective treatment, and this study showed benefits in a majority of patients, other physicians – including allergists – aren’t convinced.
How Do I Find an Alpha-Gal Specialist Near Me?
Primary care physicians tend to be generalists who know a bit about a whole lot of medical conditions. So when you are diagnosed with a condition that is still relatively new, it’s even more likely that your regular doctor will only have limited advice. You can find a global list of physicians who are alpha-gal experts as well as a list of patient-recommended physicians on the Alpha-Gal Information website.
Do You Have a Question About Alpha-Gal Not Answered Here?
Have a question not addressed here? Drop me an email at hello@sagescott.com and let me know what’s on your mind!
Thank you for sharing!

